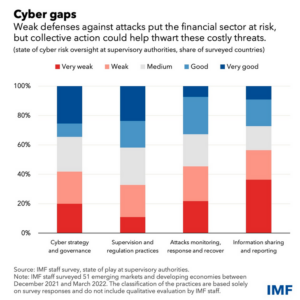
The International Monetary Fund sent an urgent call in 2023, urging financial institutions to update their cybersecurity protocols. Why? Because the number of cyberattacks against banks are on the rise. And yet, most financial institutions haven’t done everything they can to counter the threat. Consider the results from their latest survey:
- 56 percent of the countries polled do not have a national cybersecurity strategy for their central banks or supervisory authorities
- 42 percent of financial institutions don’t have a dedicated cybersecurity or technology risk unit
- 64 percent do not require cybersecurity training and testing
- 48 percent do not have proper rules and policies set for their cybersecurity
- 54 percent said they don’t have a suitable protocol for cybercrime
As you can see from the chart below, the number of organizations that feel good about their cybersecurity protections is depressingly low. So that begs the question: what’s to be done about it? At Integris, we have a financial institution division specializing in helping community banks and credit unions with their IT operations. Here are some critical cybersecurity protections we don’t recommend you skip.
Top Five Cybersecurity Measures Financial Institutions Can’t Afford to Ignore
Many tools can help keep banks and credit unions safe. These tools are often are requested by regulators and cyber risk insurers. The list of tools is long. But here are a few that we think can be most effective for your organization.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): A layered security approach requires a combination of two or more credentials to verify a user’s identity. It should be used on all accounts, especially for high-privileged users, to help protect critical systems.
User Activity Monitoring (UAM): This tool monitors and tracks end-user behavior on devices and networks and helps detect and stop insider threats (unintentional or malicious).
Data Encryption: Security method rendering information (in transit or at rest) unreadable when accessed without proper authorization, making it much more difficult for cybercriminals to steal data.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): This tool blocks data from leaving the network unauthorized. DLP prevents accidental or malicious data sharing that could put the organization at risk.
Threat Intelligence Feeds: This resource shows trends in malicious activity, typical cyberattacks, and habits of attackers within networks to help organizations stay current and prepared for the latest threats.
Cybersecurity for Financial Institutions: The Human Factor
Identifying and implementing the right technology tools will help keep customer data safe and avoid losses of resources and reputation. And while these measures are crucial to cybersecurity, people ultimately make such strategies effective.
Building a security culture through ongoing education and training is one of the best defenses against cyberattacks and part of the holistic approach needed in today’s environment to keep banks and financial institutions safe. Contact us for a free consultation to learn more about what cybersecurity strategy can do for your financial institution.